
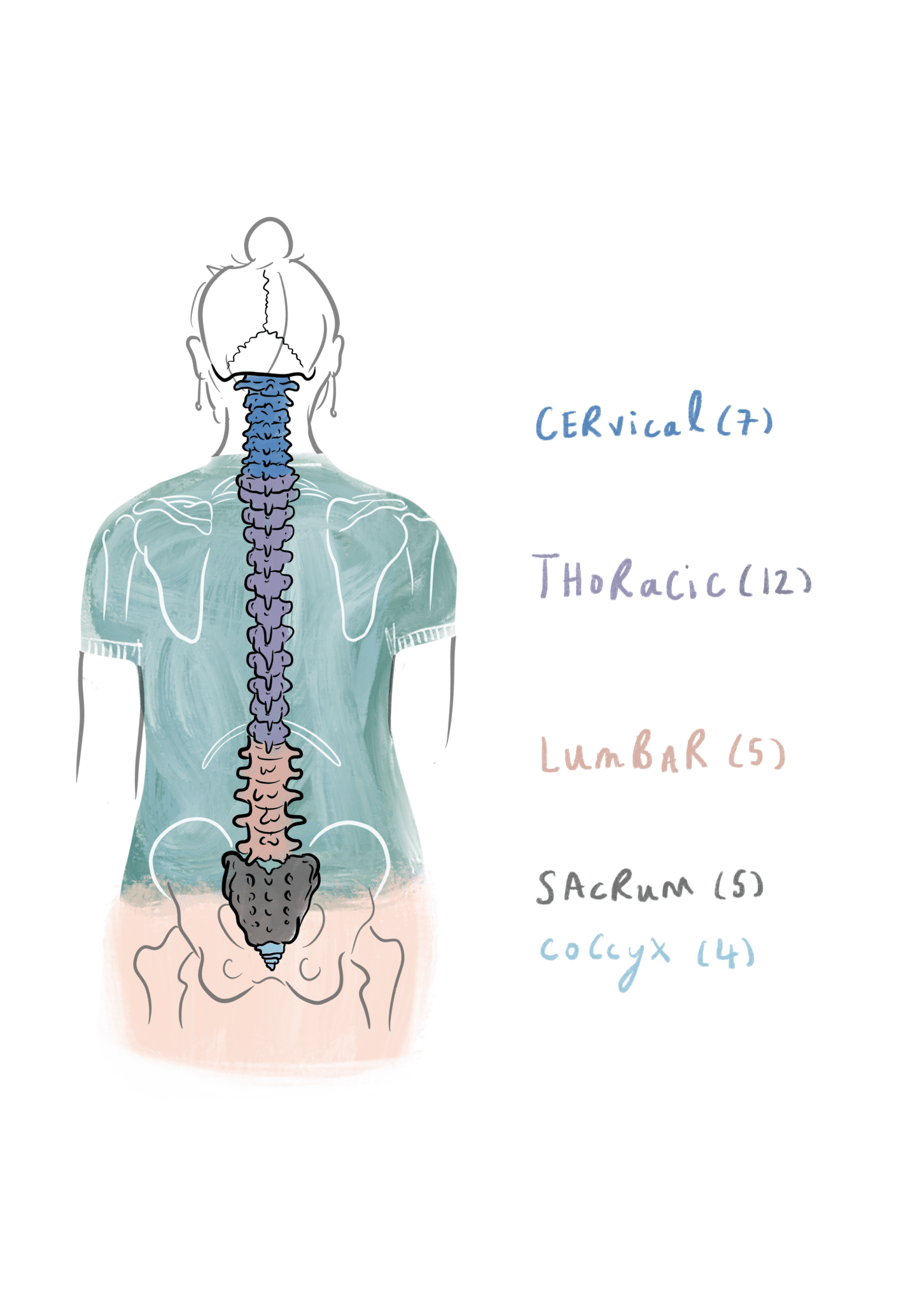
The remaining segmental ligaments include the supraspinous and interspinous ligaments, which lie between the spinous processes and resist lumbar flexion. The segmental ligaments include the ligamentum flavum, which is perforated when performing a lumbar puncture. The posterior longitudinal ligament resists lumbar flexion. The anterior longitudinal ligament resists lumbar extension, translation, and rotation. Two longitudinal ligaments lie anterior and posterior to the vertebral body. The primary function of the lumbar disc is shock absorption. It is composed of an internal gelatinous nucleus pulposus and an external fibrous annulus fibrosus. The lumbar disc is a fibrocartilaginous structure that is seated between two vertebral body endplates. The pars interarticularis is the location of the lamina between the superior and inferior articular processes and is prone to the development of stress fractures (spondylolysis) in the growing spine. These joints lie in the sagittal plane and participate in flexion and extension of the lumbar spine. This joint occurs between the superior articular process of a vertebra and the inferior articular process of the vertebra immediately cephalad. The superior and inferior articular processes create the zygapophyseal joints (aka facet joints). The transverse processes extend laterally, serving as attachment points for ligaments and musculature. At the junction between the pedicles and laminae, four articular processes and two transverse processes reside. From the junction of the two laminae, the spinous process extends posteriorly.

The pedicles resist motion and transmit forces from the posterior elements to the vertebral body. Immediately dorsal to the vertebral body lie two pedicles that attach to the laminae. These include the vertebral body and the dorsal structures termed the posterior elements. Įach lumbar vertebra consists of multiple components. This curvature is variable in degree and transfers the upper body mass over the pelvis to allow for efficient bipedal motion. From a lateral view, the lumbar spine has a concave curvature, referred to as the lumbar lordosis. The lumbar spine allows for diverse types of truncal motion, including flexion, extension, rotation, and side bending. This arrangement allows for the communication of information from the central nervous system to the lower extremities and vice versa. The lumbar vertebrae form a canal that serves to protect the spinal cord and spinal nerves. The lumbar vertebrae (L1-L5) are much larger when compared to other regions of the vertebral column, which allow them to absorb axial forces delivered from the head, neck, and trunk. First, the lumbar spine assists in supporting the upper body. doi: doi: 10.There are three main functions of the lumbar spine. Preoperative epidural steroid injections are not associated with increased rates of infection and dural tear in lumbar spine surgery. Koltsov JCB, Smuck MW, Alamin TF, Wood KB, Cheng I, Hu SS. Postural awareness and its relation to pain: validation of an innovative instrument measuring awareness of body posture in patients with chronic pain. The effect of lumbar stabilization and walking exercises on chronic low back pain: A randomized controlled trial. Comparison of longitudinal sciatic nerve movement with different mobilization exercises: an in vivo study utilizing ultrasound imaging. Efficacy Comparison of the Exercises Based on the Lumbar Extension and Flexion in Low Back Pain.Įllis RF, Hing WA, McNair PJ.

Low back pain response to pelvic tilt position: an observational study of chiropractic patients. Minicozzi SJ, Russell BS, Ray KJ, Struebing AY, Owens EF. Effect of seven sessions of posterior- to-anterior spinal mobilisation versus prone press-ups in non-specific low back pain – randomized clinical trial. Perspectives on the treatment of lumbar disc degeneration: the value proposition for a cell-based therapy, immunomodulatory properties of discogenic cells and the associated clinical evaluation strategy. Silverman LI, Heaton W, Farhang N, et al. National Library of Medicine MedlinePlus. Surgery versus conservative care for persistent sciatica lasting 4 to 12 months. Vertebral Compression Fractures.īailey CS, Rasoulinejad P, Taylor D, et al. Spine Injuries and Disorders.Īmerican Association of Neurological Surgeons. Comparative Clinical Effectiveness of Nonsurgical Treatment Methods in Patients With Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Schneider MJ, Ammendolia C, Murphy DR, et al. Hip and lumbar spine physical examination findings in people presenting with low back pain, with or without lower extremity pain. Prather H, Cheng A, Steger-May K, Maheshwari V, Van Dillen L.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
